New Technology Uncovers Hidden Mitochondrial DNA Mutations
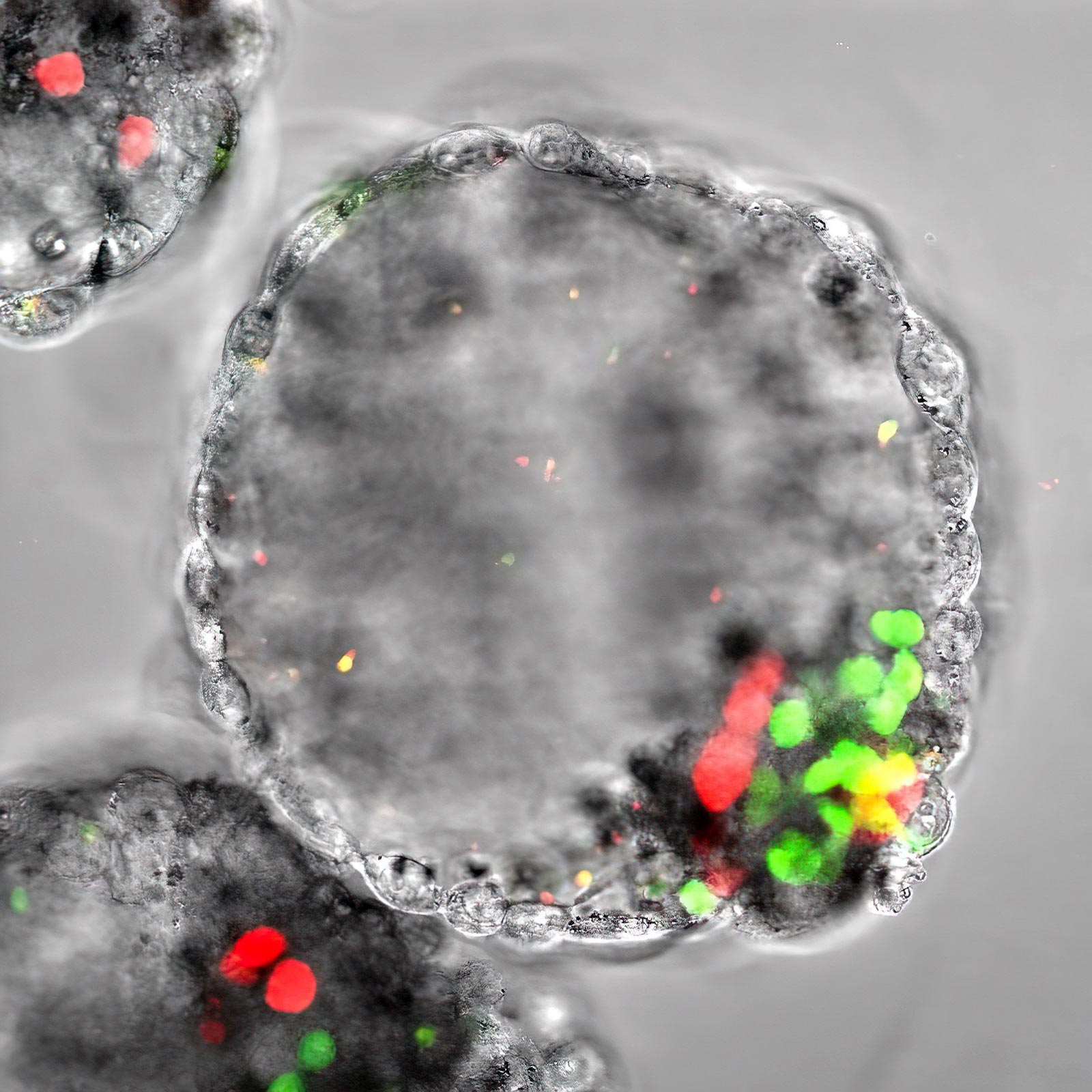
A human blastocyst-like artificial embryo named blastoid displaying the existence of an enveloping layer of more-embryonic cells, a blastocoel-like cavity, epiblast cells (environmentally friendly, offering rise to the potential embryo) and hypoblast cells (pink, giving increase to the upcoming amnion). iMiGSeq was employed to sequence mtDNA in a one blastoid to model the dynamics of mtDNA mutations all through human embryogenesis. Credit score: © 2023 KAUST Mo Li
A superior-throughput single-mobile one-mitochondrial genome sequencing know-how regarded as iMiGseq has presented new insights into mutations of mitochondrial
An international team of researchers, led by KAUST stem cell biologist Mo Li, has now quantitatively depicted the genetic maps of mtDNA in single human oocytes (immature eggs) and blastoids (stem cell-based synthetic embryos).[1] This has disclosed molecular features of unusual mtDNA mutations that cause maternally inherited conditions.
Mitochondria, the “powerhouses” of cells, perform a crucial part in cellular conversation and metabolism. Human mtDNA is a circular genome made up of 37 genes, encoding 13 proteins and a noncoding D-loop area. Heteroplasmic mutations, inherited from egg cells, can lead to congenital ailments, like maternally inherited Leigh syndrome, and are linked with late-onset advanced disorders.
“Next-technology sequencing has been made use of to sequence mtDNA and implicated heteroplasmic mutations as major contributors to metabolic disease. Yet the comprehension of mtDNA mutations continues to be restricted owing to the constraints of traditional sequencing technologies,” states lead creator Chongwei Bi.
“Our new iMiGseq system is substantial mainly because it enables complete sequencing of unique mtDNA in single cells, making it possible for for impartial, higher-throughput base-resolution examination of whole-length mtDNA,” states Bi. iMiGseq resolves quite a few important inquiries in the field.
Making use of third-technology nanopore sequencing know-how, the researchers have characterized mtDNA heteroplasmy in one cells and described the genetic options of mtDNA in solitary oocytes. They have examined mtDNA in induced pluripotent stem cells derived from patients with Leigh syndrome or neuropathy, ataxia or retinitis pigmentosa (NARP). This has revealed elaborate styles of pathogenic mtDNA mutations, which include solitary nucleotide variants and significant structural variants. “We ended up capable to detect scarce mutations with frequencies far underneath the traditional detection threshold of a person per cent,” suggests Mo Li.
In yet another experiment using the new technological innovation, iMiGseq exposed the prospective threats of surprising massive boosts in the frequency of off-focus on mutations, recognised as heteroplasmy, in a mitochondrial genome enhancing system referred to as mitoTALEN – a genome editing tool that cuts a specific sequence in mitochondrial DNA. It is utilised to slash a mutation that brings about mitochondrial encephalomyopathy and stroke-like episodes syndrome in affected individual-derived induced pluripotent stem cells.
“This highlights the pros of entire-size mtDNA haplotype examination for knowing mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy change other distant mtDNA genetic variants may possibly be unintentionally affected by the modifying of a genetically linked condition-related mutation and there is a need for ultrasensitive solutions to assess the protection of enhancing tactics,” states Li.
The scientists also utilised iMiGseq to evaluate solitary human oocytes from wholesome donors and one human blastoids, synthetic embryos made from stem cells, to identify unusual mutations undetectable with typical future-era sequencing. These small-level heteroplasmic mutations, possibly inherited via the woman germline, are joined to mitochondrial ailments and cancer.[2]
The iMiGseq method delivers a novel implies to precisely depict the total haplotypes of person mtDNA in single cells, presenting an excellent system for conveying the trigger of mitochondrial mutation-related disorders, analyzing the safety of many mtDNA modifying strategies and unraveling the links amongst mtDNA mutations, growing old and the improvement of complicated conditions.
References:
- “Quantitative haplotype-fixed assessment of mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in Human solitary oocytes, blastoids, and pluripotent stem cells” by Chongwei Bi, Lin Wang, Yong Admirer, Baolei Yuan, Samhan Alsolami, Yingzi Zhang, Pu-Yao Zhang, Yanyi Huang, Yang Yu, Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte and Mo Li, 4 April 2023, Nucleic Acids Exploration.
DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad209 - “Single-mobile particular person full-duration mtDNA sequencing by iMiGseq uncovers surprising heteroplasmy shifts in mtDNA editing” by Chongwei Bi, Lin Wang, Yong Enthusiast, Baolei Yuan, Gerardo Ramos-Mandujano, Yingzi Zhang, Samhan Alsolami, Xuan Zhou, Jincheng Wang, Yanjiao Shao, Pradeep Reddy, Pu-Yao Zhang, Yanyi Huang, Yang Yu, Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte and Mo Li, 31 March 2023, Nucleic Acids Investigate.
DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad208
